What Automobile Parts Are Made by Forging?
The most prominent application of forged components is in the automobile industry. Forging alters the metal’s shape placed on a die by applying pressure via heavy presses or rollers. There are many types of forging techniques, and each has its highs and lows. Therefore, manufacturers choose a forging method based on the required geometry.
An automobile also consists of machined and casted parts, but the most important are forged components. Because of their high strength and durability, forged parts can easily withstand the harsh conditions of the automotive environment.
Some forging techniques for forging automobile parts include press, drop, upset, and rolled ring forging. The following excerpt contains a list of forged components used in automobiles.
Automobile Components That Are Commonly Forged
Forged automobile components are used because of their tensional strength and reliability. Moreover, the overall cost of component construction is significantly less than other manufacturing methods.
Crankshafts
One of the most common parts made through forging is the crankshaft, a vital engine component. It is responsible for converting the linear motion of the pistons into the rotational motion needed to turn the wheels. Therefore, it requires increased strength and durability.
Forged crankshafts can bear the stresses and high temperatures of the engine, making them a preferred choice in high-performance and racing applications.
Connecting Rods
Connecting rods are another vital engine component that is commonly made through forging. The connecting rods join the pistons to the crankshaft and are subjected to extreme loads and stresses during engine operation.
Forged connecting rods survive heavy loads better than cast or machined rods, resulting in increased performance and reliability.
Steering Components
Steering components are also frequently made through forging. Forged steering arms, pitman arms, and tie rods can survive the stresses of steering and suspension, providing a safe and consistent driving experience.
These parts are typically made from high-strength steel alloys, which can endure bending and twisting without degrading.
Wheels
Wheels are another automotive component commonly made through forging. Forged wheels are more robust and lighter than cast wheels, providing improved performance and handling. The forging process also allows for intricate designs and shapes to be created, resulting in visually striking and unique aftermarket wheel designs.
Axles
Axles are one of the primary automotive components made through forging. Forged axles are sturdier than machined ones and can withstand stresses and loads better. Their resistivity towards stresses and strains makes them a preferred choice for high-performance and heavy-duty applications.
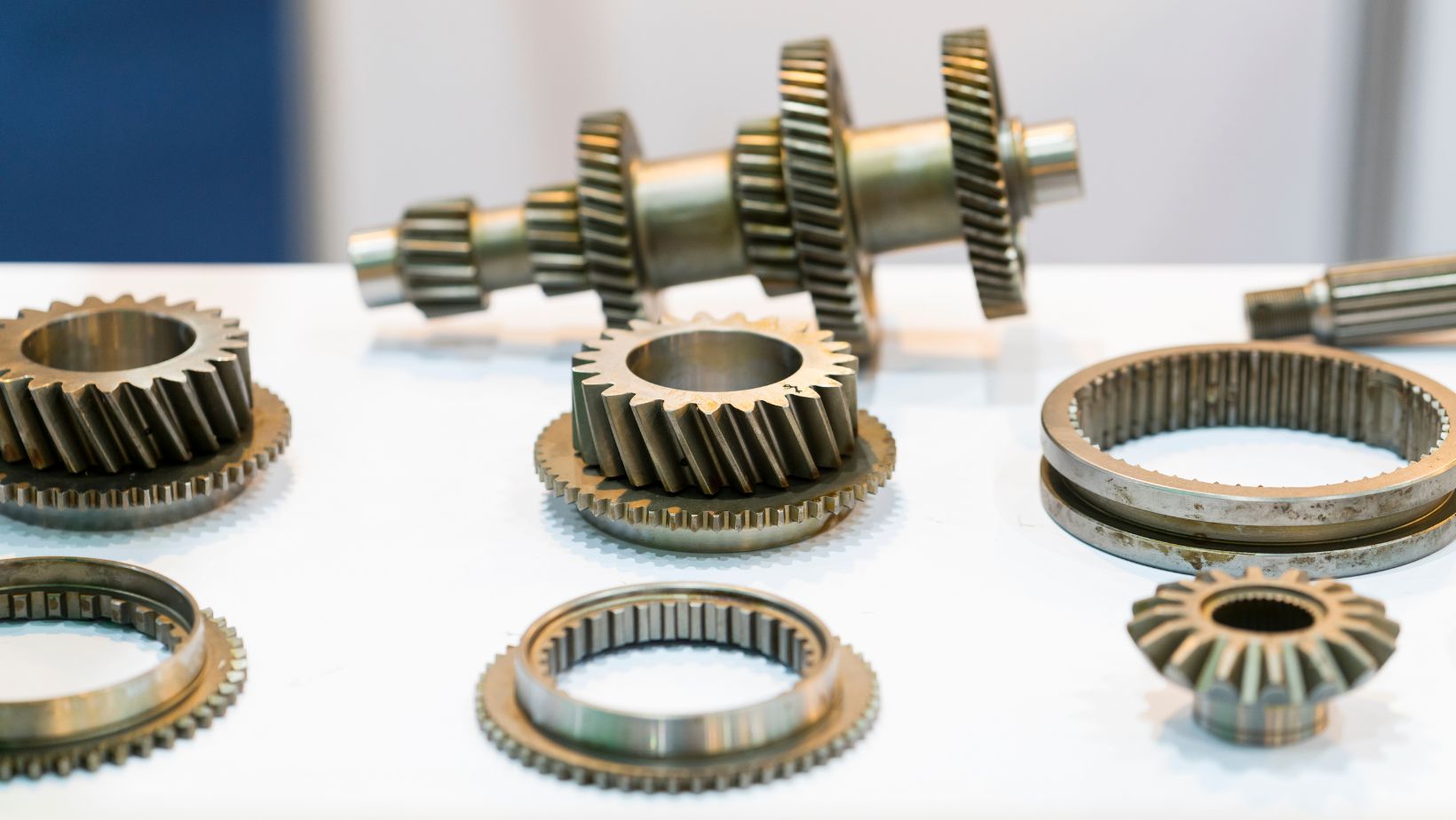
Transmission Gears
Forging is a versatile metal-working process and allows the creation of complexly shaped components like transmission gears. Forged gears are highly resistant to heavy weights and last for years.
In addition, to their reliability, forged transmission gears also improve engine performance as the power flows systematically. A smooth-running engine increases fuel efficiency and elevates driving experiences thanks to the precision construction of forged transmission gears.
Some Other Components
In addition to these major components, many other automotive parts are made through forging. Suspension components, such as control arms and spindles, are often made through forging. Additional elements, like bolts, nuts, and fasteners, are also common applications of forging.
Final Verdict
Forging finds significant application in the automotive industry as it produces high-strength and durable components that can endure harsh encounters during the vehicle’s operation.
From engine components to wheels, axles, and transmission gears, forging is a reliable method for producing high-quality automobile parts. As technology advances, the forging techniques will likely evolve to deliver more accuracy.