Overclocking is increasing the clock speed of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) to improve its performance. Even though overclocking can speed up processing, it can produce much heat. Heatsinks are made to dissipate heat away from the CPU and other components to avoid damage and maintain stable performance.
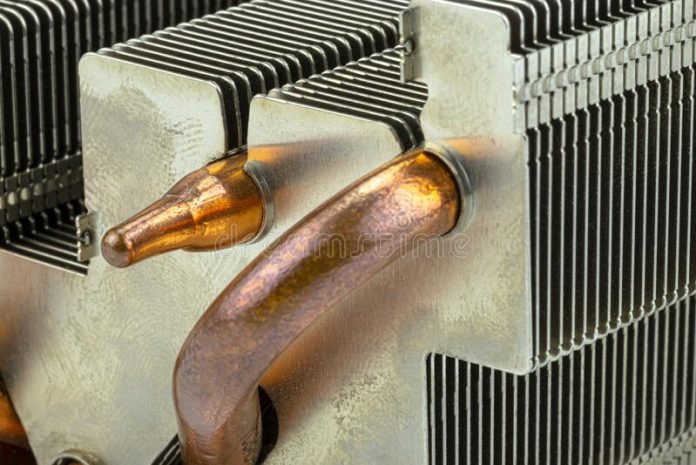
One of the most debated topics regarding heatsinks is Aluminium vs copper heat dissipation, as these two materials are the most commonly used for this purpose. Which material is better for overclocking, though both have advantages and disadvantages? Let’s look more closely.
Factors to Consider
Temperature Conduction
The ability of a heatsink to transfer heat away from the CPU is one of the most crucial aspects to consider when selecting one. At room temperature, copper has a thermal conductivity of 385 W/(mK), whereas aluminium has a thermal conductivity of 205 W/(mK).
This indicates copper heatsinks are more effective at transferring heat away from the CPU than aluminium heatsinks. A more effective heatsink can help keep the CPU cool and prevent damage when overclocking because higher clock speeds produce more heat.
Cost
Undoubtedly, the cost is also a factor when choosing a heatsink. Copper heatsinks cost more than aluminium heatsinks because copper is a more expensive material.
It’s crucial to remember that the heatsink’s price is only a small portion of the overall cost of an overclocking build. Purchasing a high-quality heatsink, whether made of copper or Aluminium, can help ensure consistent performance and guard against CPU damage, ultimately saving you money.
Effectiveness
Copper heatsinks may be more dense and conductive than aluminium, but that doesn’t always make them better for overclocking. The size, shape, fan configuration, and thermal paste used to affix the heatsink to the CPU are just a few of the variables that affect a heatsink’s efficiency.
Many premium aluminium heatsinks are available that are just as good at dissipating heat as their copper counterparts. The secret is to select a heatsink made explicitly for overclocking, one with a sizable surface area, numerous heat pipes, premium fans, and thermal paste.
Density
The density of the material used for the heatsink is an additional consideration. Copper is a denser substance with a density of 8.96 g/cm3 compared to aluminium’s 2.70 g/cm3.
As a result, copper heatsinks are frequently heavier than aluminium ones, which may be a drawback if you’re designing a system that needs to be portable or lightweight. However, a copper heatsink’s additional weight can also offer better stability and durability, which is advantageous for demanding tasks like overclocking.
Selecting the Best Heatsink for Overclocking
Suppose you’re building a high-performance system for demanding tasks like gaming, video editing, or scientific computing and don’t mind the added cost and weight. In that case, a copper heatsink may be the best option as it can withstand higher temperatures and transfer heat away from the CPU more effectively. However, an aluminium heatsink may be a better choice if you’re building a lightweight, portable, or budget-conscious system. It’s crucial to consider the size, shape, number of heat pipes, quality of fans and thermal paste, and specific CPU and cooling system requirements when selecting a heatsink for overclocking to ensure stable performance and prevent system damage.
Other materials like graphite and vapour chambers can offer better thermal conductivity than copper or aluminium heatsinks. However, they are usually more expensive and unnecessary for most overclocking purposes.
Conclusion
For overclocking, copper and aluminium are suitable materials for heatsinks. The decision between copper and aluminium ultimately depends on your needs and requirements. A copper heatsink might be the best option if you are constructing a high-performance system and don’t mind the extra cost and weight. If you are constructing a system that is more portable or on a tighter budget, an aluminium heatsink might be a better option. In either case, spending money on a suitable heatsink is essential for consistent performance and preventing damage to your CPU.